Link Token price manipulation claimed by researchers in Anchain.ai, a blockchain security company. The recent market drop of the chainlink token Link has a possible pump and dump scam angle.
In a report by security advisor anchain.ai, the company claims that the recent drop in chainlinks token value was an indication of a scam. The scam is called a pump and dump.
According to Anchain.ai, Chainlink’s Token price drop shows a clear indication of a scam. The token is part of the Line Network, the whatsapp of Japan. The researchers believe that this represents a classic case of a pump and dump scam.
In these kind of scams, a particular asset is pumped into the market drastically increasing its value. Investors who are not aware of the scam may invest in the asset hoping to capitalize on the sudden rise. When the value gets to a certain point, they sell off their stocks, dumping it into the market in bulk. This results in a drastic drop in value and investors stand to lose all of their investment.
What is Chainlink?
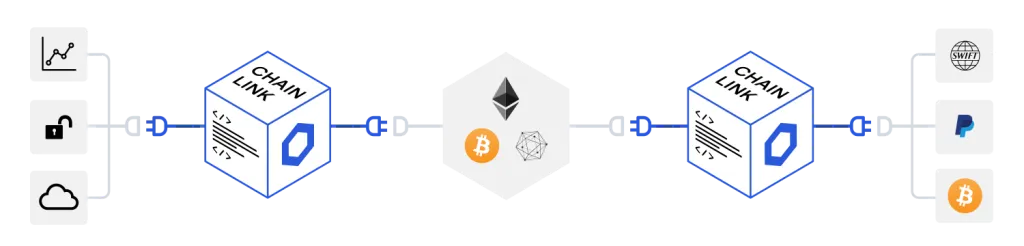
Launched by the San Francisco fintech company SmartContract in June 2017, Chainlink is described by its developers as a secure blockchain middleware that intends to connect smart contracts across blockchains by allowing smart contracts to access key off-chain resources such as data feeds, web APIs, and traditional bank account payments.
The Chainlink developers believes that although smart contracts may revolutionize many industries by replacing the need for traditional legal agreements, the underlying consensus protocols related to blockchain technology results in smart contracts being unable to effectively communicate with external systems.
The Chainlink ecosystem revolves around the LINK token and the LINK network. Through the release of APIs and other platforms, the developers plan to enhance the applicability and usability of smart contracts across the business world.
However, according to the developers of Chainlink there are a number of drawbacks to the current structure of smart contracts on the blockchain. For example, due to the fact that smart contracts are based on information secured on a blockchain, and due to the way that consensus is reached by miners around blockchain-based transaction data, smart contracts are unable to interact with external resources such as data feeds, API’s or traditional banking systems.
The way this problem is traditionally solved is through the use of a blockchain middleware called an “oracle”. Chainlink proposes a secure oracle network that is fully decentralized by being based on blockchain technology, allowing connectivity between smart contracts and external (or off-chain) resources.
What are Oracles?
Oracles are necessary because blockchains cannot directly access data outside of their network. Oracles are defined as an ‘agent’ that finds and verifies real-world occurrences and submits this information to a blockchain to be used in smart contracts. It provides the external data that is necessary to trigger smart contracts execution when pre-defined conditions (such as perhaps a received payment or a price fluctuation) are reached.
Because oracles are third party services with a centralized point of control, and which are not part of the blockchain consensus mechanism, the issues that arise in relation to smart contracts is whether data received from an oracle is trustworthy.
Because smart contracts may be self-executing based on certain conditions, it is essential that the oracles are providing accurate and trustworthy information. For example, if inaccurate data on the price of a stock is transmitted into the blockchain and relied upon by a smart contract, the smart contract could execute the wrong function based on this bad data.
Some oracles rely on notarization to verify their data, while others rely on the manual human input of unstructured data. However, these types of oracles are flawed according to the Chainlink developers: the former because the need for verification may be recursive; the latter because it would be costly, resource intensive and would not be able to provide real-time data.
Oracles
The developers of Chainlink intend to solve this issue by creating a decentralized oracle network for smart contracts to securely interact with resources external to the blockchain, such as cryptographically secure data feeds, as well as facilitating inter-operability in between blockchains.
According to the developers, the Chainlink network will allow anyone who has a data feed or any other API can provide them directly to smart contracts in exchange for Chainlink tokens. Such persons are referred to as Node Operators and allow such data providers (or, for example, payment providers or service providers), to sell their API based services directly to a smart contract in exchange for LINK tokens.
The developers suggest that this decentralized infrastructure allows for data, off-chain payments and APIs into a smart contract in a way that is scalable, secure and auditable.